-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Home
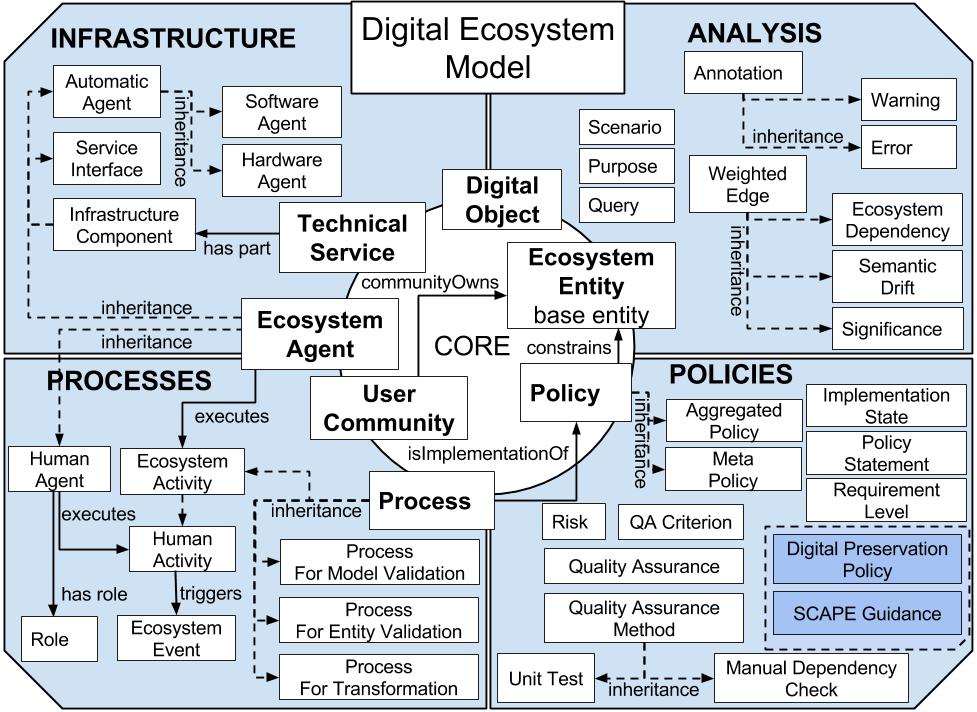
Here a description of the different DEM entities, possible attributes and relations is given. The relations have prefixes that indicate to which ontology they refer to: LRM corresponds to Linked Resource Model (LRM) concepts, DEM items are the different DEM sub-ontologies and SCAPE-preservation refers to the imported preservation ontology from the DEM-Policy model. We do not include all LRM based dependencies and entities within this reference. The following picture summarises the different sub-models and the entities:
The core model consists of five main entity types which allow to define basic principles that are valid for all inheriting entities of the model, such as the integration of the LRM versioning mechanism for all entities, or relations which can have any DEM entity as target. The following figure shows the elements:
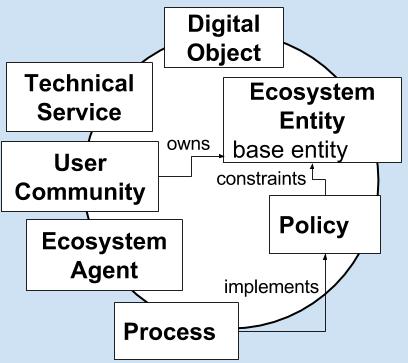
A Digital Object represents any item that is available digitally. It can be an aggregation of other digital objects.
An Ecosystem Activity is an activity executed by an EcosystemAgent. Add a specific activity class from the LRM as second base class to record provenance information, e.g. LRM:ActivityStarted, LRM:ActivityStopped, LRM:ActivitySuspended, LRM:ActivityResumed.
An Ecosystem Agent is an agent in the ecosystem that performs activities.
The Ecosystem Entity is a helper entity. All the DEM classes inherit from this entity. This helps to apply common principles to the entities, e.g. a policy may constrain all entities within a DEM. It is normally not necessary to use this entity for a scenario.
A Process is a description of linked steps on how to transform an input to a certain output.
A Policy is a plan that defines the desired state inside a digital ecosystem. A policy describes the 'what' (guidelines) and not the 'how' (implementation).
A Technical Service is an infrastructure consisting of hard- and software components and service interfaces. A Technical Service provides services for the DE, which can be accessed by its service interfaces. A Technical Service consists of infrastructure components, digital objects, processes, and other technical services.
We use User Community to mean a designated community similar to the OAIS definition “Designated Community” (OAIS 2012, p1-11 (https://public.ccsds.org/pubs/650x0m2.pdf)), while in the DEM a User Community it is not bound to a definition by the Archive. "Designated Communities" is a concept of the OAIS to denote a group of users which influence the criteria for successful preservation. In DEM a User Community does not only “understand a particular set of information”, but can play an active role in the model.
| Entity | ObjectProperty | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| DEM-Core:DigitalObject | checksum | A checksum for digital objects, e.g. MD5 or SHA hash. |
| DEM-Core:Policy | hasConflictIDAttribute | Attribute for conflicting policies detection. |
| DEM-Core:Process | function | A description of the function the process performs, or its purpose. |
| DEM-Core:Process | function | A description of the function the process performs, or its purpose. |
| DEM-Core:Process | hasLink | Link to the BPMN implementation. |
| From Entity… | Relation | Explanation | …to Entity |
|---|---|---|---|
| All DEM entities | managedBy | This entity is managed by a process. | DEM-Core:UserCommunity |
| All DEM entities | ownedBy (inverse of owns) | A community can own ecosystem entities. | DEM-Core:UserCommunity |
| DEM-Core:DigitalObject | derivedFrom | An entity can be derived from a higher level entity. It is therewith not a sub entity of the higher level entity, but a derivation of it. | DEM-Core:DigitalObject |
| DEM-Core:Policy | constrains | Refers to an ecosystem entity which is constrained by the policy. | All DEM entities |
| DEM-Core:Policy | derivedFrom | An entity can be derived from a higher level entity. It is therewith not a sub entity of the higher level entity, but a derivation of it. | DEM-Core:Policy |
| DEM-Core:Policy | hasMandator | The entity that mandates or generates the policy. The mandator could be also a reference to a legal requirement (in case that a policy is mandated by a legal requirement) or a directive. | All DEM entities |
| DEM-Core:Policy | replaces (inverse replacedBy) | Refers to an old policy which is replaced by this policy. | DEM-Core:Policy |
| DEM-Core:Process | hasInput | The input of the process. | All DEM entities |
| DEM-Core:Process | hasOutput | The output of the process. | All DEM entities |
| DEM-Core:Policy | isEnforcedBy (inverse isImplementationOf) | Process can be the implementation of a Policy. | DEM-Core:Process |
| DEM-Core:Process | isImplementationOf (inverse isEnforcedBy) | A process can be an implementation of a policy. | DEM-Core:Policy |
| DEM-Core:Process | manages (inverse managedBy) | A process can manage all ecosystem entities. | All DEM entities |
| DEM-Core:Process | runsOn | Relation to the technical service infrastructure on which the process is executed. | DEM-Core:TechnicalService |
| DEM-Core:Policy | targetCommunity | The community for which the policy has been designed. | DEM-Core:UserCommunity |
| DEM-Core:UserCommunity | communityOwns (inverse ownedByCommunity) | A community can own ecosystem entities. | All DEM entities |
The policy sub-ontology builds up on the policy model from PERICLES as described in Deliverable 5.3 p.51-71. The policy model contains a specification of the policy entity and a QA (quality assurance) part, which is responsible for validating and ensuring that policies are correctly applied.
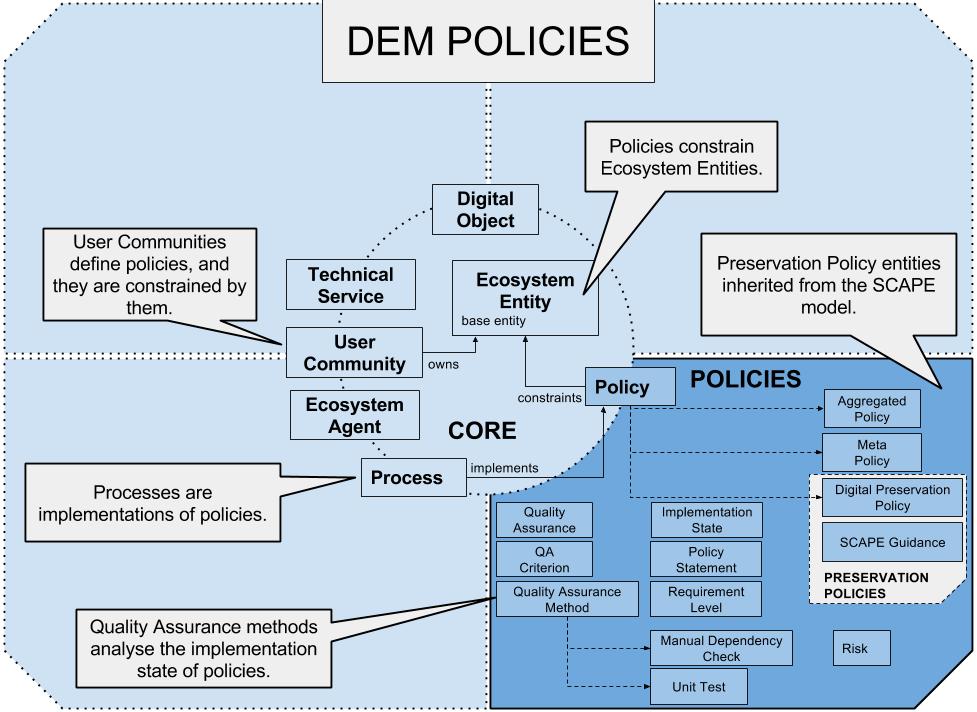
An Aggregated Policy consists of other policies.
The Implementation State defines how deeply a policy is currently implemented (implemented, partially implemented, unimplemented, unimplementable).
The Manual Dependency Check is a quality assurance method which needs a human agent to verify a dependency. (Subclass of “DEM-Policy:QualityAssuranceMethod”)
A Meta Policy is a policy about policies which creates, deletes, modifies, enables, disables policies inside the digital ecosystem (Subclass of “DEM-Core:Policy”).
A Policy Level defines the level of a policy, e.g. guidance, procedure, control, etc.
A Policy Statement is a detailed definition of the policy contents (formal or not formal).
A Quality Assurance Criterion is a condition-action, a rule, a unit test or other formal definition of QA methods (Subclass of “DEM-Core:Policy”).
A method for quality assurance (Subclass of “DEM-Core:Process”).
A unit test for quality assurance (Subclass of “DEM-Policy:QualityAssuranceMethod”).
We use Requirement Level following the definition of RFC 2119. This can be used to define what the desired level of compliance of a policy is (must, must not, required, shall, shall not, should, should not, recommended, may, optional).
Describes a risk of a policy.
| Entity | ObjectProperty | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| DEM-Core:Policy | classification | Type of policy (TBC), such as: data management, format, access, ... |
| DEM-Core:Policy | hasPolicyType | Links a policy entity to a policy type. |
| DEM-Core:Policy | hasValidationStatus | Links a policy entity to a validation status. |
| DEM-Core:Policy | validFrom | Defines a start date of a policy. |
| DEM-Core:Policy | validTo | Defines an expire date of a policy. |
| DEM-Core:Policy | hasProcessSequence | Ordered sequence of processes which implement a policy. |
| DEM-Policy:PolicyStatement | format | Formal format: if so what language used; or non formal (free text). |
| DEM-Policy:PolicyStatement | language | The language used for the criteria definition (natural, ReAL, SWRL, etc.). |
| DEM-Policy:RequirementLevel | complianceLevel | Describes the level of compliance. |
| From Entity… | Relation | Explanation | …to Entity |
|---|---|---|---|
| DEM-Core:Policy | addQACriterion | Refers to a quality assurance criterion for a policy. | DEM-Policy:QualityAssuranceCriterion |
| DEM-Core:Policy | hasImplementationState | Current state of the policy: How well the policy is currently implemented. | DEM-Policy:ImplementationState |
| DEM-Core:Policy | hasMetaPolicy | The policy has a meta policy. | DEM-Policy:MetaPolicy |
| DEM-Core:Policy | hasPolicyLevel | Links a policy entity to a policy level. | DEM-olicy:PolicyLevel |
| DEM-Core:Policy | hasPolicyStatement | Refers to the policy statement. | DEM-Policy:PolicyStatement |
| DEM-Core:Policy | hasRequirementLevel | The policy has a requirement level. | DEM-Policy:RequirementLevel |
| DEM-Core:Policy | hasRisk | The policy has a risk. | DEM-Policy:Risk |
| DEM-Core:Process | ensuresQACriterion | Links to a QA criterion, which is ensured by this process. | DEM-Policy:QualityAssuranceCriterion |
| DEM-Policy:ManualDependencyCheck | verifiedBy | Links a manual dependency check to the agent that executes the manual QA verification. | DEM-Core:EcosystemAgent |
| DEM-Policy:QualityAssuranceCriterion | assuresQualityOf | The quality assurance definition assures the quality of a designated policy linked via this relation. | DEM-Core:Policy |
| DEM-Policy:QualityAssuranceCriterion | hasImplementation | Links a quality assurance criterion to a quality assurance method that implements the criterion. | DEM-Policy:QualityAssuranceMethod |
| DEM-Policy:QualityAssuranceMethod | verifies | A quality assurance method verifies that a quality assurance criterion or test is fulfilled regarding the related ecosystem entity. | All DEM entities |
The DEM Policy Model is supplemented by preservation policy elements which has been developed by the SCAPE project. The following elements have been imported as entities to the model:
- SCAPE-Preservation:GuidancePolicyAccess
- SCAPE-Preservation:GuidancePolicyAuthenticaticity
- SCAPE-Preservation:GuidancePolicyFunctionalPreservation
- SCAPE-Preservation:GuidancePolicyOrganisation
- SCAPE-Preservation:DigitalPreservationPolicy
- SCAPE-Preservation:GuidancePolicyMetadata
- SCAPE-Preservation:GuidancePolicyRights
- SCAPE-Preservation:GuidancePolicyStandards
- SCAPE-Preservation:GuidancePolicyBitPreservation
- SCAPE-Preservation:GuidancePolicyTrustworthyDigitalRepositories
For a definition of the SCAPE-Preservation Policy entities, please see: http://wiki.opf-labs.org/display/SP/Policy+Elements.
The purpose of the DEM Process model is to capture which Ecosystem entity is processed by a certain process and which Ecosystem Agent is part of the process. The process flow is not modelled, a link to an implementation (e.g. to a BPMN file) can be added.
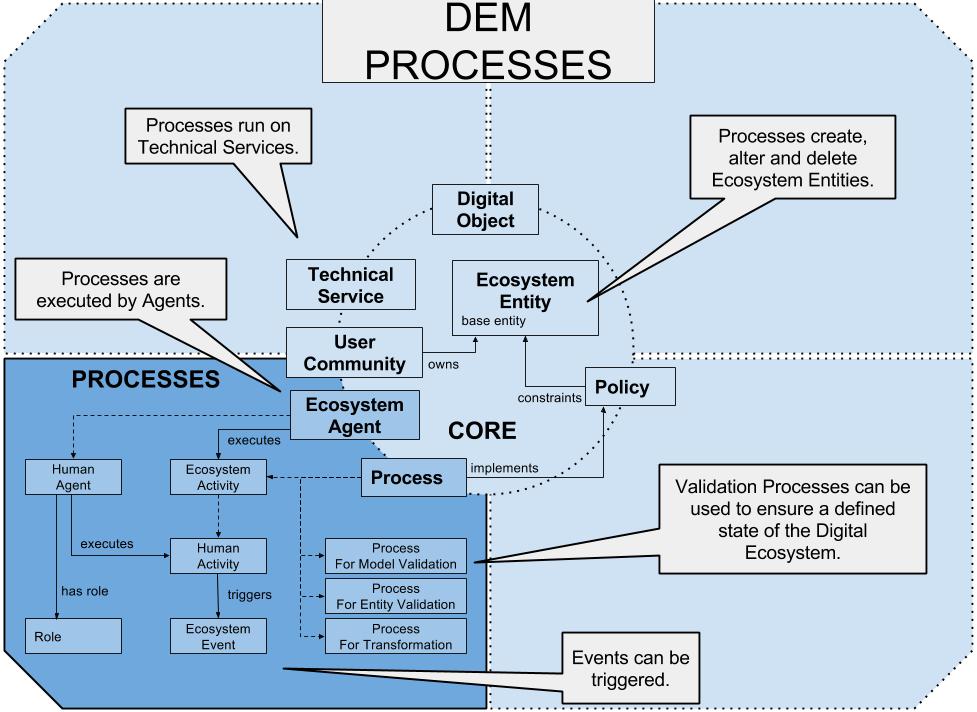
An Aggregated Process consists of other processes. This entity is used to build a process hierarchy with a tree structure (Subclass of “DEM-Core:Process”).
An event triggered by an EcosystemActivity. Add a more specific LRM event class as second base class to describe the event type, in more detail e.g. lrm:RecurringEvent, lrm:ChangeEvent, lrm:CreationEvent, etc.
A human activity is an ecosystem activity which is executed by a HumanAgent.
A human agent in the ecosystem executing human activities.
The implementation of a process. (Subclass of “DEM-Core Digital Object”)
A ProEV is the second process of the process triple {ProMV,ProEV,ProT} which is recommended to be modelled as process implementation of a policy. A ProEV operates on entity level. Its purpose is to check if an entity fulfils the policy constraints, and to pipe each entity which fails the validation into ProT. Therefore the ProEV is called either by ProMV, or in case of an entity process to verify the entity state. A ProEV can be an aggregated resource of sub-ProEV. (Subclass of “DEM-Core:Process”)
A ProMV is the first process of the process triple {ProMV,ProEV,ProT} which is recommended to be modelled as process implementation of a policy. A ProMV operates on CORE_MODEL level. Its purpose is to get the set of entities which are constrained by a policy from the CORE_MODEL, and to pass each entity into a ProEV. Therefore the ProMV is called in case of policy changes, or after a huge CORE_MODEL process. A ProMV can be an aggregated resource of sub-ProMV. (Subclass of “DEM-Core Process”)
A ProT is the third process of the process triple {ProMV,ProEV,ProT} which is recommended to be modelled as process implementation of a policy. A ProT operates on entity level and transforms an entity from an invalid state into a valid state regarding the constraints of a policy. ProT gets the entity input from ProEV in case of the occurrence of an invalid entity. A ProT can be an aggregated resource of sub-ProT.
Humans can have a designated role.
An input- or output slot is linked to a process and defines which entity types can be passed as input or output of the process.
| Entity | ObjectProperty | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| DEM-Core:Process | hasAutomationState | Links an Automation State to a process. |
| DEM-Process:AggregatedProcess | processSequence | Order of execution of sub-processes of an aggregated process |
| DEM-Process:Implementation | hasMimeType | Defines the mime type of an implementation. |
| DEM-Process:Slot | hasInputSlot | Specifies an output slot of a process. |
| DEM-Process:Slot | hasOutputSlot | Specifies an input slot of a process. |
| DEM-Process:Slot | slotNumber | The number of the slot as input or output parameter of the process. |
| DEM-Process:Slot | slotTemplate | The entity template / type which instances can be passed to this process slot. |
| From Entity… | Relation | Explanation | …to Entity |
|---|---|---|---|
| All DEM entities | ownedByPerson (inverse of personOwns) | A Human can own ecosystem entities. | DEM-Process:HumanAgent |
| DEM-Core:Digital Object | hasAuthor | Defines the author of the Digital Object. | DEM-Process:HumanAgent |
| DEM-Core:Ecosystem Agent | hasRole | Assigns a role to a community or to an agent. | DEM-Process:Role |
| DEM-Process:HumanAgent | personOwns (inverse of ownedByPerson) | A human agent can own ecosystem entities. | All DEM entities |
| DEM-Core:Policy | responsible | Refers to the responsible person for the application of the policy | DEM-Process:HumanAgent |
| DEM-Core:Process | hasImplementation | Links an implementation entity to a Process. | DEM-Process:Implementation |
| DEM-Core: User Community | hasRole | Assigns a role to a community or to an agent. | DEM-Process:Role |
| DEM-Process:Slot | passesOutputTo | The output of a typed process output slot is passed to a process input slot of the same type. | DEM-Process:Slot |
| DEM-Process:Slot | receivesInputFrom | The typed process input slot receives the output from an output slot of the same type. | DEM-Process:Slot |
The DEM Infrastructure model has the purpose to model infrastructure components such as hardware and software, interfaces and the corresponding agents.
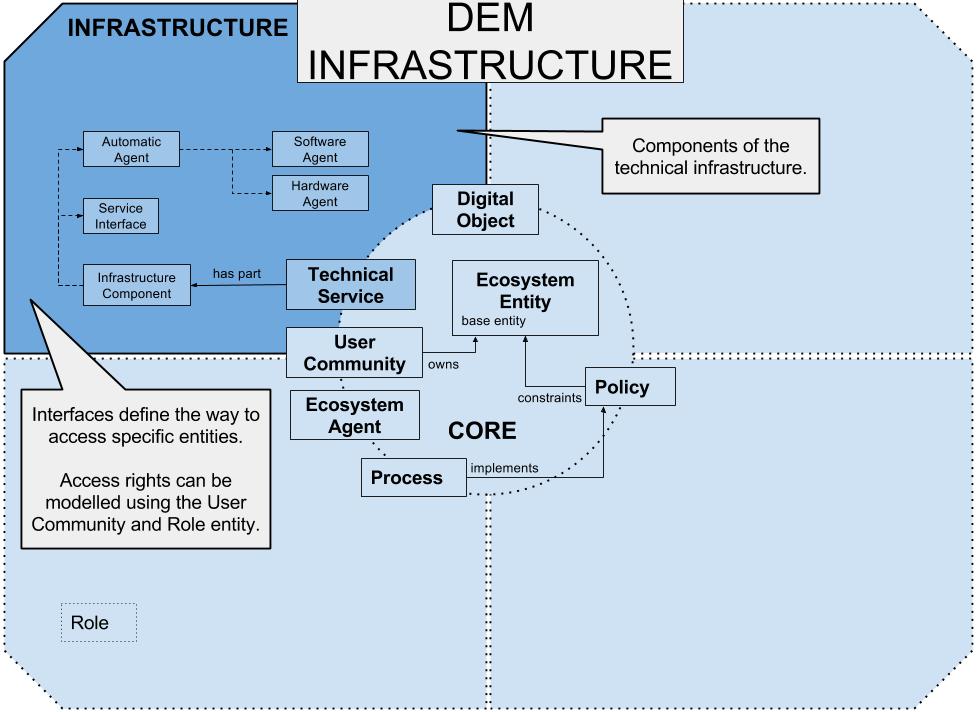
An automatic agent is a non-human agent in the infrastructure of a technical system (Subclass of “DEM-Infrastructure InfrastructureComponent”).
An automatised activity is an ecosystem activity which is executed by a Hard- or SoftwareAgent.
An infrastructure component which is realised as hardware agent (Subclass of “DEM-Infrastructure AutomaticAgent”).
A component of the technical infrastructure. An infrastructure component is part of a technical service.
The interface of a technical system. Ecosystem agents use a service interface to access a technical system (Subclass of “DEM-Infrastructure InfrastructureComponent”).
A software agent infrastructure component (Subclass of “DEM-Infrastructure AutomaticAgent”).
| From Entity… | Relation | Explanation | …to Entity |
|---|---|---|---|
| DEM-Core:DigitalObject | accessedVia | This component is accessed via a service interface. | DEM-Infrastructure:ServiceInterface |
| DEM-Core:Process | accessedVia | This component is accessed via a service interface. | DEM-Infrastructure:ServiceInterface |
| DEM-Core:TechnicalService | accessedVia | This component is accessed via a service interface. | DEM-Infrastructure:ServiceInterface |
| DEM-Infrastructure:InfrastructureComponent | accessedVia | This component is accessed via a service interface. | |
| DEM-Infrastructure:ServiceInterface | isUsedBy | This relation can be used to express that an agent uses an interface to access technical services, as well as that a community uses such an interface. | |
| DEM-Infrastructure:ServiceInterface | providesAccessTo | The service interface provides access to digital objects, technical services, processes, or infrastructure components as hardware- or software agents. | DEM-Infrastructure:InfrastructureComponent, DEM-Core:Process, DEM-Core:DigitalObject, DEM-Core:TechnicalService |
| DEM-Infrastructure:AutomaticAgent | runsOn | A software or hardware agent runs on a server. | DEM-Core:TechnicalService |
The DEM can be seen as a multigraph. The entities are nodes and their relations are edges. The DEM Analysis model provides entities and special relations for edges which can be used to record additional meta-information on top of a DEM instance. The DEM Analysis model can therefore be used for arbitrary graph analysis models. Note that the DEM provides the required structure for model analyses, but not the algorithms that perform the analyses.
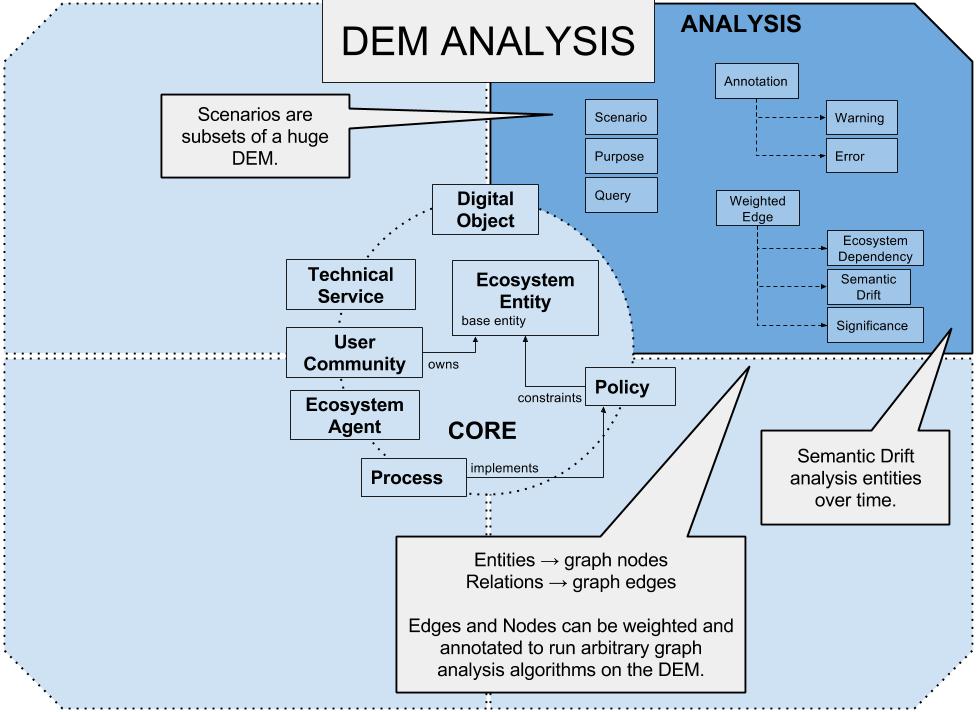
Annotation of an entity or a Weighted Relation.
The Cost entity can be added to entities to mark costs. It can be used to add values, while the meaning of this values can be added with a DEM-Analyses:Annotation entity.
A dependency in the digital ecosystem (Subclass of “DEM-Analysis:WeightedRelation”).
Can be used to mark an error of entities, e.g. a process might flag an error (Subclass of DEM-Analysis Annotation). The kind of error is not further specified by the DEM and can be defined via a DEM-Analyses:Annotation entity.
The purpose allows to categorise the functions or relations of entities. E.g. preservation process has the purpose to keep the objects.
Either an external query submitted by a human agent or an internal process-to-process query to propagate control requests (Subclass of “DEM-Core:Process”).
The scenario entity is the view on the ontology. A scenario contains a collection of several entities. Each scenario can have unique weighting of the entities.
This weighted relation points from an Ecosystem Entity to an earlier version of the same Ecosystem Entity, or to another Ecosystem Entity with huge semantic similarities. It is used to express the semantic drift between these two entities (Subclass of “DEM-Analysis:WeightedRelation”).
A weighted relation which expresses the significance of an Ecosystem Entity for another Ecosystem Entity, e.g. for a Scenario or a Purpose (Subclass of “DEM-Analysis:WeightedRelation”).
Can be used to mark an warning of entities (Subclass of “DEM-Analysis:Annotation”). The Warning entity might be produced by processes or notifications.
This entity corresponds to a weighted edge in the graph. It can also be used to weight entities by pointing the "from" and the "to" to the same entity.
###Object Properties
| Entity | ObjectProperty | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| DEM-Analysis:WeightedRelation | hasValue | Assigns a weight to a weighted relation. |
| From Entity… | Relation | Explanation | …to Entity |
|---|---|---|---|
| All DEM entities | hasAnnotation (inverse of annotates) | The ecosystem entity has an annotation. | DEM-Analysis:Annotation |
| All DEM entities | hasCost (inverse of cost of) | The ecosystem entity has specified costs | DEM-Analysis:Cost |
| All DEM entities | hasPurpose (inverse of purpose of) | The ecosystem entity has a specific purpose. | DEM-Analysis:Purpose |
| All DEM entities | taggedBy (inverse of tags) | The ecosystem entity has a tag | DEM-Analysis:Tag |
| DEM-Analysis:Annotation | annotates (inverse of hasAnnotation) | Annotates an ecosystem entity. | All DEM entities |
| DEM-Analysis: Cost | costOf (inverse of has cost) | Specifies the amount of costs of an entity | All DEM entities |
| DEM-Analysis:Purpose | purposeOf (inverse of hasPurpose) | The purpose refers to an ecosystem entity. | All DEM entities |
| DEM-Analysis:Tag | tags (inverse of taggedBy) | Can be used for tagging entities; provides a method for grouping of entities without binding them to a Purpose or Scenario. | All DEM entities |
| DEM-Analysis:WeightedRelation | calculatedBy | The value of the weighted relation was calculated or measured by the referred entity. | All DEM entities |