Transcribe input from your microphone and turn it into key presses on a virtual keyboard. This allows you to use speech-to-text on any application or window system in Linux. In fact you can use it on the system console.
With assistant mode you can take this a step further and control you desktop entirely with voice!
VoxInput is meant to be used with LocalAI, but it will function with any OpenAI compatible API that provides the transcription endpoint or realtime API.
- Speech-to-Text Daemon: Runs as a background process to listen for signals to start or stop recording audio.
- Audio Capture: Records audio from the microphone or any other device, including audio you are listening to.
- Transcription: Converts recorded audio into text using a local or remote transcription service.
- Text Automation: Simulates typing the transcribed text into an application using
dotool. - Voice Activity Detection: In realtime mode VoxInput uses VAD to detect speech segments and automatically transcribe them.
- Visual Notification: In realtime mode, a GUI notification informs you when recording (VAD) has started or stopped.
- Assistant Mode: Voice conversations with an LLM using the OpenAI Realtime API with bidirectional audio streaming, automatic speech detection, and voice responses.
- Desktop Control: In assistant mode, the LLM can execute keyboard and mouse commands through function calls to control your desktop environment.
dotool(for simulating keyboard input)- The user that runs VoxInput daemon is in the
inputuser group - You have the following udev rule
KERNEL=="uinput", GROUP="input", MODE="0620", OPTIONS+="static_node=uinput"
This can be set in your NixOS config as follows
services.udev.extraRules = ''
KERNEL=="uinput", GROUP="input", MODE="0620", OPTIONS+="static_node=uinput"
'';-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/richiejp/VoxInput.git cd VoxInput -
Build the project:
go build -o voxinput
-
Ensure
dotoolis installed on your system and it can make key presses. -
It makes sense to bind the
recordandwritecommands to keys using your window manager. For instance in my Sway config I have the following
bindsym $mod+Shift+t exec voxinput record
bindsym $mod+t exec voxinput write
Alternatively you can use the Nix flake.
Note: VOXINPUT_ vars take precedence vars with other prefixes.
Unless you don't mind running VoxInput as root, then you also need to ensure the following is setup for dotool
OPENAI_API_KEYorVOXINPUT_API_KEY: Your OpenAI API key for Whisper transcription. If you have a local instance with no key, then just leave it unset.OPENAI_BASE_URLorVOXINPUT_BASE_URL: The base URL of the OpenAI compatible API server: defaults tohttp://localhost:8080/v1VOXINPUT_LANG: Language code for transcription. The full string is used as-is (defaults to empty).LANG: Language code for transcription. Only the first 2 characters are used (defaults to empty).VOXINPUT_LANGtakes precedence if set.VOXINPUT_TRANSCRIPTION_MODEL: Transcription model (default:whisper-1).VOXINPUT_ASSISTANT_MODEL: Assistant model (default:none).VOXINPUT_ASSISTANT_VOICE: Assistant voice (default:alloy).VOXINPUT_ASSISTANT_INSTRUCTIONSorASSISTANT_INSTRUCTIONS: System prompt for the assistant model. Used to configure assistant behavior and available actions.VOXINPUT_ASSISTANT_ENABLE_DOTOOL: Enable the dotool function in assistant mode (yes/no, default: yes).VOXINPUT_TRANSCRIPTION_TIMEOUT: Timeout duration (default:30s).VOXINPUT_SHOW_STATUS: Show GUI notifications (yes/no, default:yes).VOXINPUT_CAPTURE_DEVICE: Specific audio capture device name (runvoxinput devicesto list).VOXINPUT_OUTPUT_FILE: Path to save the transcribed text to a file instead of typing it with dotool.VOXINPUT_MODE: Realtime mode (transcription|assistant, default: transcription).VOXINPUT_INPUT_SAMPLE_RATE: Sample rate for audio input in Hz (default: 24000). Used for capturing audio and for realtime API input.VOXINPUT_OUTPUT_SAMPLE_RATE: Sample rate for audio output in Hz (default: 24000). Used for realtime API output and audio playback.XDG_RUNTIME_DIRorVOXINPUT_RUNTIME_DIR: Used for the PID and state files, defaults to/run/voxinputif niether are present
Warning: Assistant mode is WIP and you may need a particular version of LocalAI's realtime API to run it because I am developing both in lockstep. Eventually though it should be compatible with at least OpenAI or LocalAI.
-
listen: Start speech to text daemon.--replay: Play the audio just recorded for transcription (non-realtime mode only).--no-realtime: Use the HTTP API instead of the realtime API; disables VAD.--no-show-status: Don't show when recording has started or stopped.--output-file <path>: Save transcript to file instead of typing.--prompt <text>: Text used to condition model output. Could be previously transcribed text or uncommon words you expect to use--mode <transcription|assistant>: Realtime mode (default: transcription)--instructions <text>: System prompt for the assistant model--no-dotool: (assistant mode only) Disable the dotool function call
./voxinput listen
-
record: Tell existing listener to start recording audio. In realtime mode it also begins transcription../voxinput record
-
writeorstop: Tell existing listener to stop recording audio and begin transcription if not in realtime mode.stopalias makes more sense in realtime mode../voxinput write
-
toggle: Toggle recording on/off (start recording if idle, stop if recording)../voxinput toggle
-
status: Show whether the server is listening and if it's currently recording../voxinput status
-
devices: List capture devices../voxinput devices
-
help: Show help message../voxinput help -
ver: Print version../voxinput ver
-
Start the daemon in a terminal window:
OPENAI_BASE_URL=http://ai.local:8081/v1 OPENAI_WS_BASE_URL=ws://ai.local:8081/v1/realtime ./voxinput listen
-
Select a text box you want to speak into and use a global shortcut to run the following
./voxinput record
-
Begin speaking, when you pause for a second or two your speach will be transcribed and typed into the active application.
-
Send a signal to stop recording
./voxinput stop
-
Start the daemon in a terminal window:
OPENAI_BASE_URL=http://ai.local:8081/v1 ./voxinput listen --no-realtime
-
Select a text box you want to speak into and use a global shortcut to run the following
./voxinput record
-
After speaking, send a signal to stop recording and transcribe:
./voxinput write
-
The transcribed text will be typed into the active application.
To create a transcript of an online meeting or video stream by capturing system audio:
-
List available capture devices:
./voxinput devices
Identify the monitor device, e.g., "Monitor of Built-in Audio Analog Stereo".
-
Start the daemon specifying the device and output file:
VOXINPUT_CAPTURE_DEVICE="Monitor of Built-in Audio Analog Stereo" ./voxinput listen --output-file meeting_transcript.txtNote: Add
--no-realtimeif you prefer the HTTP API. -
Start recording:
./voxinput record
-
Play your online meeting or video stream; the system audio will be captured.
-
Stop recording:
./voxinput stop
-
The transcript is now in
meeting_transcript.txt.
Assistant mode enables real-time voice conversations with an LLM using the OpenAI Realtime API. The assistant can respond with voice and optionally perform desktop actions through the dotool function.
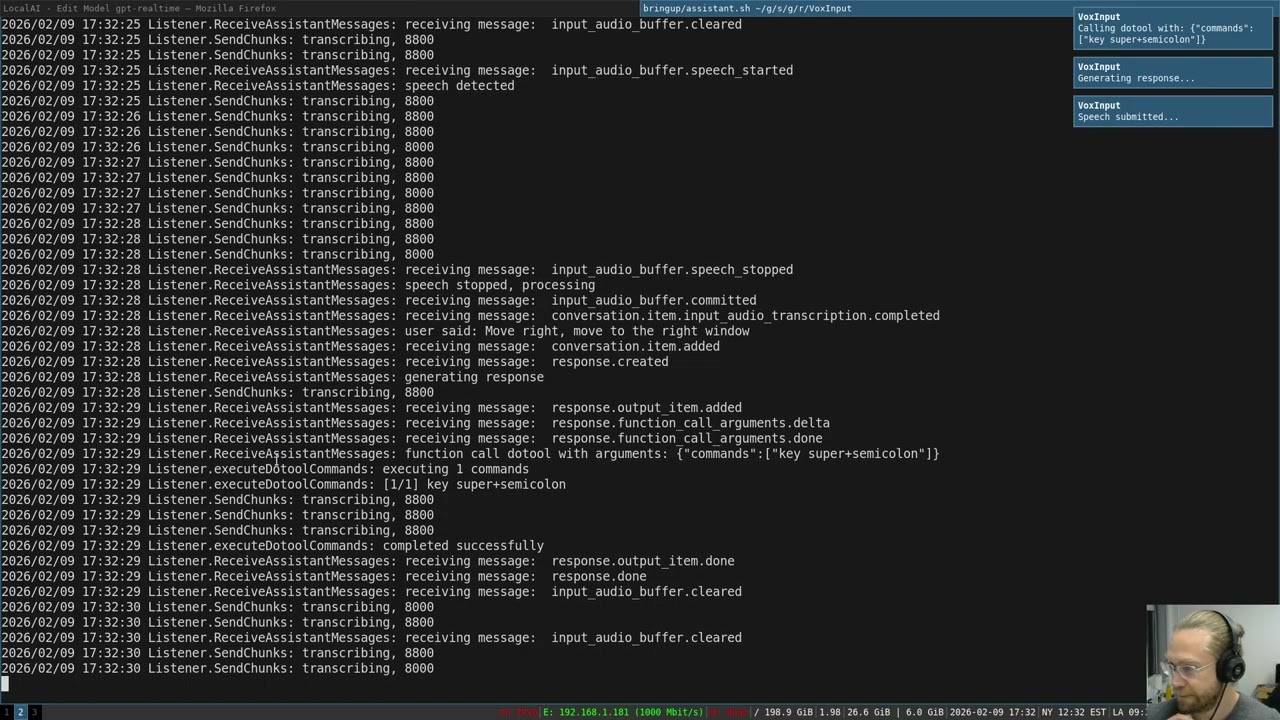
Voice assistant opening applications and controlling desktop
Real-time transcription with voice activity detection
When you start VoxInput in assistant mode:
- Start recording: Use
./voxinput recordto begin a conversation - Speak naturally: The assistant uses server-side Voice Activity Detection (VAD) to detect when you're speaking
- Get responses: The assistant responds with voice audio streamed back to you
- Desktop actions: When configured with the
dotoolfunction, the assistant can execute keyboard and mouse commands - Continue or stop: Keep talking for a back-and-forth conversation, or use
./voxinput stopto end
The assistant receives your speech in real-time, transcribes it automatically, generates a response using the configured LLM, and speaks the response back to you - all while optionally executing desktop commands when appropriate.
The VOXINPUT_ASSISTANT_INSTRUCTIONS or ASSISTANT_INSTRUCTIONS environment variable configures the assistant's behavior. This system prompt should:
- Define the assistant's role and personality
- Describe available desktop actions (when dotool is enabled)
- Provide guidance on when and how to use actions
Example instructions:
export VOXINPUT_ASSISTANT_INSTRUCTIONS="You are a desktop voice assistant. Be concise and conversational - avoid markdown or complex punctuation in speech. When asked to type or transcribe, use the dotool function with type commands. To open applications, use: key super+d, sleep 1000, type <appname>, sleep 1000, key enter. Always use lowercase for application names."When enabled (default: yes), the assistant can call a dotool function that executes an array of commands sequentially. Each command is a JSON object with:
action: The dotool command to performargs: Arguments for that command
Supported Actions:
- Keyboard:
key,keydown,keyup,type - Mouse:
click,buttondown,buttonup,wheel,hwheel,mouseto,mousemove - Timing:
keydelay,keyhold,typedelay,typehold - Sleep:
sleep <milliseconds>- pauses between commands (handled by VoxInput, not sent to dotool)
See the dotool documentation for complete command details.
Example function call from the assistant:
{
"commands": [
{"action": "key", "args": "super+d"},
{"action": "sleep", "args": "1000"},
{"action": "type", "args": "firefox"},
{"action": "sleep", "args": "1000"},
{"action": "key", "args": "enter"}
]
}Basic setup:
export OPENAI_BASE_URL=http://ai.local:8081/v1
export OPENAI_WS_BASE_URL=ws://ai.local:8081/v1/realtime
export VOXINPUT_TRANSCRIPTION_MODEL=whisper-large-turbo
export VOXINPUT_MODE=assistant
export VOXINPUT_ASSISTANT_MODEL=qwen3-4b
export VOXINPUT_ASSISTANT_VOICE=alloy
export VOXINPUT_ASSISTANT_INSTRUCTIONS="You are a helpful desktop assistant..."
./voxinput listenThen interact:
# Start conversation
./voxinput record
# Speak: "Open Firefox and search for VoxInput"
# Assistant responds with voice and executes commands
# Stop when done
./voxinput stopTo run the assistant in voice-only mode without desktop control:
# Option 1: Command line flag
./voxinput listen --mode assistant --no-dotool
# Option 2: Environment variable
export VOXINPUT_ASSISTANT_ENABLE_DOTOOL=no
./voxinput listen --mode assistantVOXINPUT_MODE=assistant- Enable assistant modeVOXINPUT_ASSISTANT_MODEL- LLM model to use (default:none- uses server default)VOXINPUT_ASSISTANT_VOICE- TTS voice (default:alloy)VOXINPUT_ASSISTANT_INSTRUCTIONS- System prompt for the assistantVOXINPUT_ASSISTANT_ENABLE_DOTOOL- Enable/disable desktop control (default:yes)VOXINPUT_INPUT_SAMPLE_RATE- Audio input sample rate (default:24000)VOXINPUT_OUTPUT_SAMPLE_RATE- Audio output sample rate (default:24000)
- Follow https://localai.io/installation/ to install LocalAI, the simplest way is using Docker:
docker run -p 8080:8080 --name local-ai -ti localai/localai:latest-
See https://localai.io/features/openai-realtime for configuring the needed pipeline model
-
Test out VoxInput:
VOXINPUT_TRANSCRIPTION_MODEL=gpt-realtime VOXINPUT_TRANSCRIPTION_TIMEOUT=30s voxinput listen
voxinput record && sleep 30s && voxinput write
The realtime mode has a UI to display various actions being taken by VoxInput. However you can also read the status from the status file or using the status command, then display it via your desktop manager (e.g. waybar). For an example see the PR which added it.
- Put playback behind a debug switch
- Create a release
- Realtime Transcription
- GUI and system tray
- Voice detection and activation (partial, see below)
- Code words to start and stop transcription
- Assistant mode
- Voice conversations with an LLM
- Submit desktop images to a VLM to allow it to click on items
- Use tool calls or MCP to allow the VLM/LLM to perform actions
- Dotool tool that allows the agent to make key presses
- MCP
- Support agent skills
SIGUSR1: Start recording audio.SIGUSR2: Stop recording and transcribe audio.SIGTERM: Stop the daemon.
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.
